Introduction:
How JSON Works? JSON is one of the most essential parts of modern web development. It is used everywhere from websites and mobile apps to cloud services and software tools. If you browse the internet, shop online, or use social media, you already interact with JSON without knowing it.
Today, almost every website and app uses JSON to send and receive data. When you request a page, log in to your account, or fetch product details, JSON helps move the information behind the scenes. It is simple, fast, and easy to understand, which makes it a top choice for developers.
Big platforms like Amazon, Facebook, and Google use JSON for their APIs. For example, product details on Amazon, user profiles on Facebook, and map data from Google Maps are all delivered through JSON, making online services smoother and faster.
This guide will teach you how JSON works, why it is essential, and how it powers web and API development. You will also see real examples, learn basic JSON syntax, and understand how developers use JSON in front-end and back-end systems. By the end, you will be confident about what JSON is and how to use it.
What Is JSON?
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight format for storing and sending data. It looks like simple text, but follows a clean and organized structure. JSON helps systems share information easily, even if they are built using different programming languages.
Developers use JSON because it is easy to read, easy to write, and very fast to process. It works smoothly with JavaScript and supports languages like Python, Java, PHP, and many more. This makes it a universal data format on the web.
JSON is also smaller than older formats, meaning websites and apps load faster and use less bandwidth. This is why JSON replaced XML in most cases.
JSON vs XML (Quick Comparison)
| Feature | JSON | XML |
| Format | Simple & clean | Complex tags |
| Speed | Fast to read | Slower |
| Use | APIs, web apps | Documents, configs |
JSON Structure Explained
A. Key JSON Components
- Keys & values “name”: “John”
- Objects { } store data in key-value pairs
- Arrays [ ] hold lists of values or objects
- Data types: strings, numbers, booleans, null
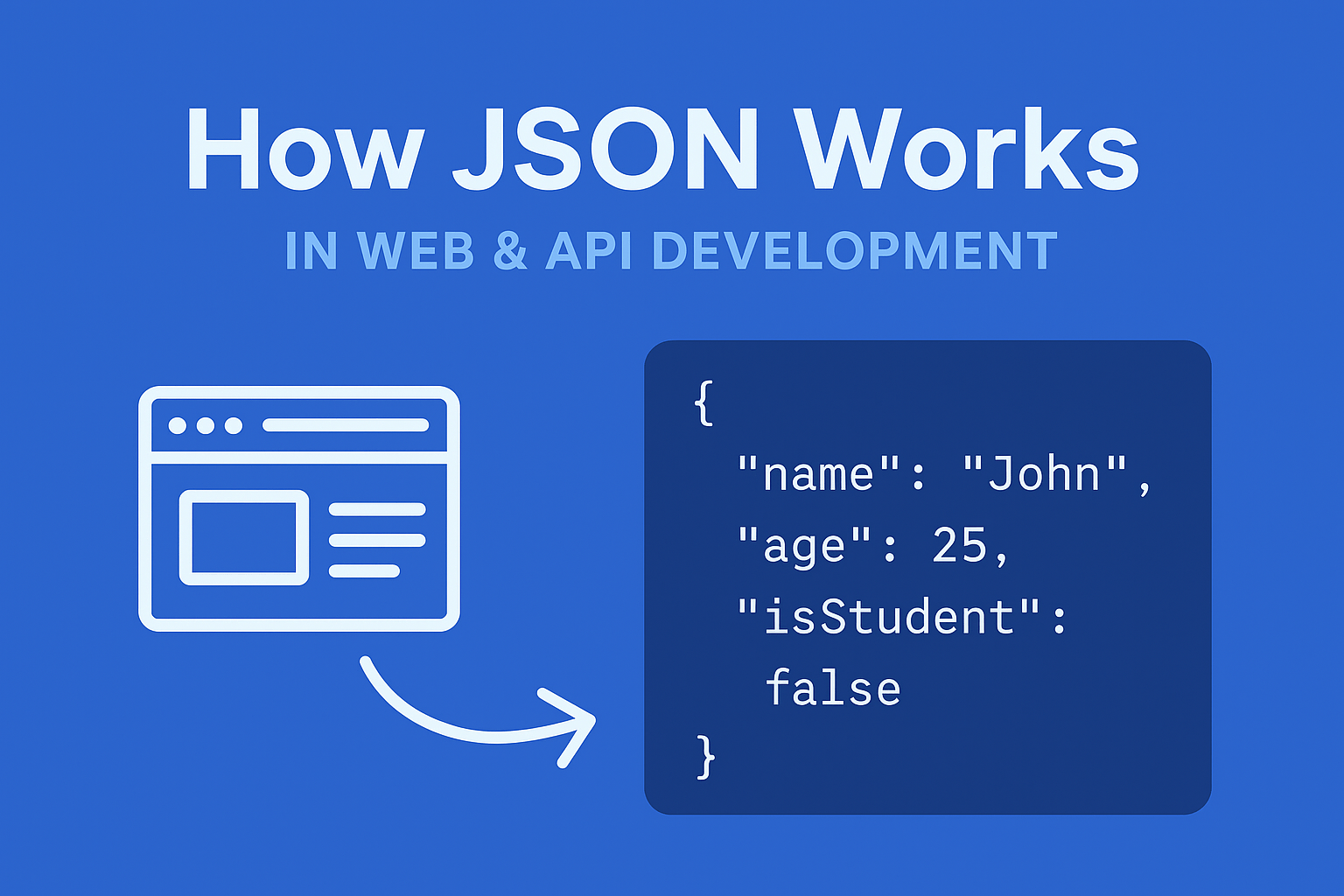
B. Basic JSON Example
| { “name”: “John”, “age”: 25, “isStudent”: false } |
How JSON Works in Web Development?
A. JSON in Front-End JavaScript
JSON helps the browser get data from a server. For example, when a website loads products or user details, it fetches JSON data using JavaScript. The browser then displays that data on the page.
B. JSON in Back-End
In back-end systems like Node.js, JSON handles user requests and talks to databases. The server reads JSON, processes it, and sends a JSON response to the front-end.
C. JSON in Local Storage & Cookies
Websites also store small data in the browser using JSON, such as login sessions, shopping carts, or user settings.
How JSON Works in API Development?
A. What an API Is
An API lets apps communicate and exchange data.
B. JSON as the API Format
Most APIs use JSON because it is easy to process and standard across platforms.
C. Request & Response Example
Request
| GET https://api.example.com/users |
JSON Response
| { “users”: [ { “id”: 1, “name”: “John” }, { “id”: 2, “name”: “Sara” } ] } |
Parsing & Using JSON
A. Parse JSON in JavaScript
| let data = JSON.parse(jsonString); |
B. Convert Object to JSON
| let json = JSON.stringify(obj); |
C. Error Handling Tips
- Always check if the JSON format is correct
- Use try…catch when parsing
JSON Best Practices
- Keep data simple & clear
- Use meaningful key names
- Avoid too many nested objects
- Validate your JSON before using
JSON vs XML: When to Use What
| Feature | JSON | XML |
| Speed | ✅ Faster | ❌ Slower |
| Readability | ✅ Easy | ❌ Complex |
| Data Type Support | ✅ Yes | ❌ Limited |
| Use Case | APIs, Web | Documents, Config files |
Common JSON Mistakes & Fixes:
- Missing commas
- Wrong quote types
- Extra commas at the end
- Case-sensitive keys
Real-World JSON Use Cases:
- Payment systems (Stripe, PayPal)
- Social platforms (Facebook, Instagram)
- Maps and routing (Google Maps)
- Weather services (Weather API)
Using JSON in API calls:
Using JSON in API calls makes exchanging data with servers easy for websites and apps. When you request information from an API, the server sends back a JSON response that contains the data in a clean, readable format.
For example, when you open an e-commerce app, it fetches product details in JSON. Developers can then parse this data and display it on the screen using JavaScript or any programming language. JSON is lightweight, fast, and works across all platforms, which is why most modern APIs use it. Simply send a request, receive JSON, and use it in your application. It’s that simple.
Conclusion:
JSON is the backbone of modern web and API communication. It allows websites, apps, and servers to exchange information smoothly and quickly. You see JSON at work whenever you log in, shop online, or use a mobile app.
In this guide, you learned what JSON is, how it works, and why developers depend on it. You also saw real examples, basic syntax, and tips to use JSON correctly in both front-end and back-end development.
Understanding JSON is essential for building modern applications. Start experimenting with simple JSON files, call free APIs, and practice parsing data in JavaScript. With regular practice, JSON will become a natural skill in your coding journey.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What is JSON used for in web development?
To exchange data between the browser and server.
2. How do APIs use JSON?
APIs send and receive data in JSON format.
3. Is JSON better than XML?
Yes, for most web tasks it’s faster and cleaner.
4. Can browsers read JSON directly?
Yes, JavaScript can easily read and show JSON data.
5. What languages support JSON?
Almost all JavaScript, Python, PHP, Java, C#, and more.