Introduction:
In the world of data sharing and programming, JSON and YAML are two names that frequently appear. Both are data serialization formats that help store, organize, and exchange information between systems in a clean and structured way. Although they serve the same purpose, their style, structure, and use cases differ significantly.
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is widely used in web development, APIs, and mobile applications. It’s simple, lightweight, and designed to be easily read by machines. Many programming languages natively support JSON, which makes it the go-to choice for developers when working with online data or APIs.
YAML (YAML Ain’t Markup Language), on the other hand, focuses on human readability. It’s commonly used in configuration files, DevOps tools, and server setups because it looks clean and easy to understand. YAML allows comments, supports indentation, and feels more natural when editing manually.
In this article, we’ll explore the 10 critical differences between JSON and YAML, complete with examples and practical explanations. By the end, you’ll know exactly when to use each format and how to choose the one that best fits your project.
What is JSON? (With Example)
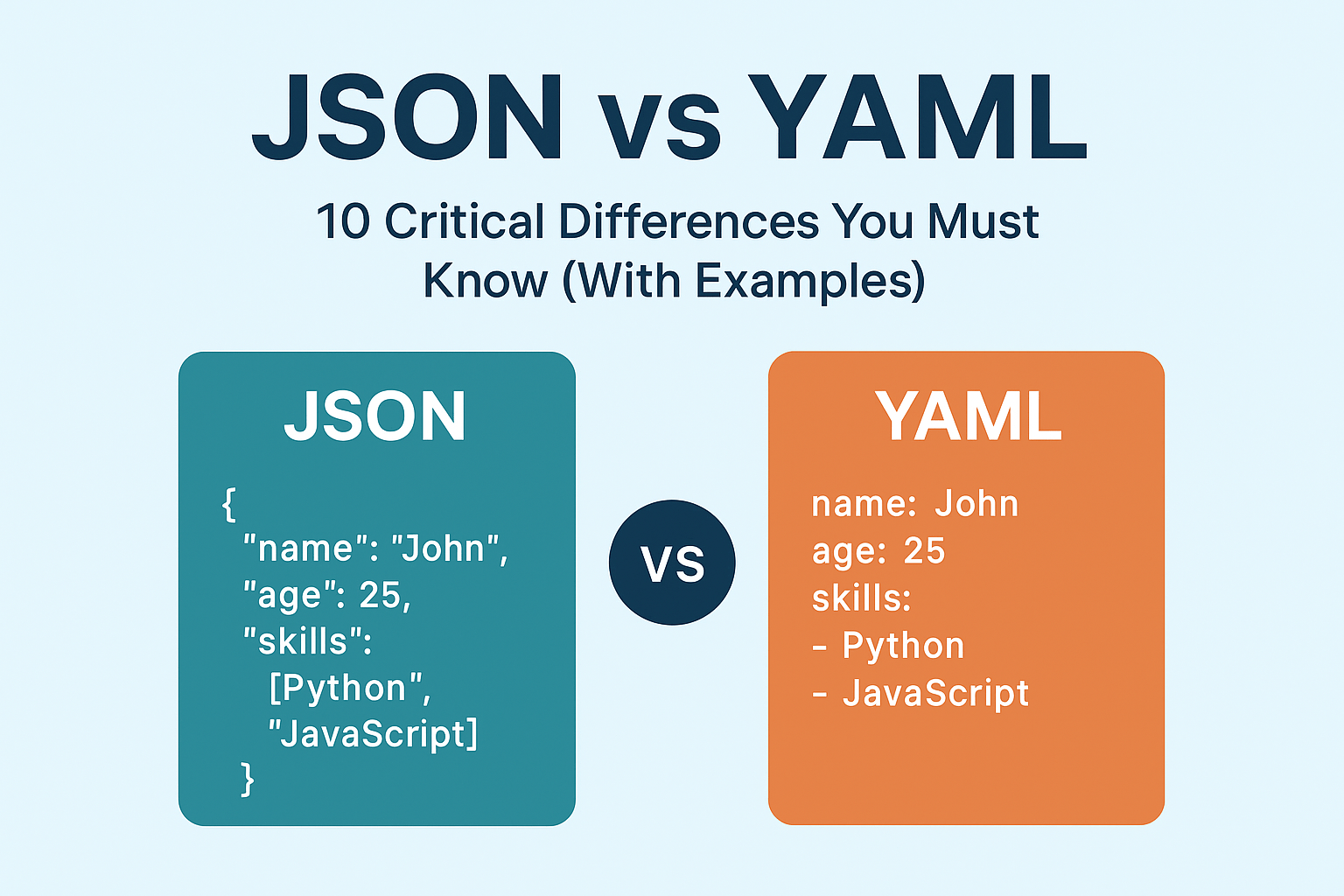
JSON or JavaScript Object Notation is one of the most widely used data serialization formats.
It’s simple, lightweight, and perfect for exchanging data between web servers and clients.
Example JSON code:
| { “name”: “John”, “age”: 25, “skills”: [“Python”, “JavaScript”] } |
What is YAML? (With Example)
YAML, short for YAML Ain’t Markup Language, focuses on human readability.
It’s widely used in configuration files for tools like Docker, Kubernetes, and GitHub Actions.
Example YAML code:
| name: John age: 25 skills: – Python – JavaScript |
JSON vs YAML Syntax and Structure
Syntax is one of the most significant differences between the JSON and YAML formats.
- JSON uses braces {}, brackets [], and commas.
- YAML depends on indentation and colons (:) for structure.
Example JSON vs YAML Syntax:
| {“city”: “New York”} city: New York |
JSON vs YAML: 10 Key Differences Explained
1. Readability
YAML is designed for humans, JSON is designed for machines.
That’s why YAML is more readable for configuration files.
2. Performance and Speed
- JSON files are faster to parse and load because they use a simpler structure.
- YAML can be slower, but it is more flexible.
3. Comments Support
- JSON: ❌ No comments allowed.
- YAML: ✅ Comments allowed using #.
4. Compatibility with Programming Languages
- Both are supported in many languages, but JSON is more universally compatible.
5. Conversion Between JSON and YAML
You can easily convert JSON to YAML or vice versa using online tools.
Example Tools:
- JSON to YAML Online Converter
- YAML to JSON Converter
6. File Formats
Both JSON and YAML have their own file extensions:
- JSON → .json
- YAML → .yml or .yaml
7. Use Cases: When to Use JSON or YAML
Use JSON for:
- APIs
- Web apps
- Data serialization
Use YAML for:
- Configuration files
- CI/CD pipelines
- DevOps automation
8. Pros and Cons
| Format | Pros | Cons |
| JSON | Fast, Universal, Lightweight | Hard to read, no comments |
| YAML | Easy To Read, Supports Comments | Slower, depends on indentation |
9. Similarities Between JSON and YAML
- Both are text-based data formats.
- Both support key-value pairs.
- Both are used for storing structured data.
10. Example Comparison Table
| Feature | JSON | YAML |
| Syntax | { } and [ ] | Indentation |
| Readability | Moderate | High |
| Comments | No | Yes |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Compatibiltiy | High | Moderate |
Can you use JSON in YAML?
Yes, you can actually use JSON inside YAML, because YAML is a superset of JSON. This means that every valid JSON file is also a valid YAML file. You can take a JSON object, paste it into a YAML file, and it will still work perfectly without any changes.
For example, this JSON code is also valid YAML:
| { “name”: “John”, “age”: 25, “skills”: [“Python”, “JavaScript”] } |
YAML will read and interpret it the same way. This makes it easy to convert JSON to YAML or mix them when needed.
However, while YAML supports JSON syntax, the reverse isn’t true. JSON does not support YAML’s indentation style or features, such as comments and references. So, if you prefer machine-friendly files, stick with JSON; however, if you want readable configurations, YAML offers more flexibility.
Conclusion:
Both JSON and YAML are powerful and widely used data formats, but they shine in different situations. If you want something that’s fast, lightweight, and compatible with all programming languages, go with JSON. It’s perfect for APIs, data exchange, and web applications.
If your goal is readability and easy-to-edit configuration files, then YAML is the better choice. It looks cleaner, supports comments, and is excellent for DevOps, servers, and automation tools like Docker or Kubernetes.
In simple terms, use JSON for machines and YAML for humans. Each format has its own strengths, and understanding the key differences helps you choose the right one for your next project. Regardless of which one you use, both make managing and sharing data simpler, smarter, and more efficient in modern programming.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What is the main difference between JSON and YAML?
JSON uses symbols like { } while YAML uses indentation.
2. Which is easier to read?
YAML is easier for humans to read and understand.
3. Can I convert JSON to YAML?
Yes, use a JSON to YAML online converter tool.
4. Is YAML better for configuration?
Yes, YAML supports comments and indentation, making it an excellent choice for configuration files.
5. Which is faster?
JSON is faster to load and parse.